Ну раз уж @Areku выложил свой Конспект “Теории ограничения систем Голдратта” Уильяма Деттмера, пора бы и мне выложить свой. У меня он не такой лаконичный и не на русском, но тем не менее тоже имеется. С интересными дополнительными материалами, ссылками и прочим.
Почему на английском? Потому что читаю на английском и переводить на русский как-то очень уж напрягает. К тому же преподавание английского обязывает практиковать язык.
Перевести можно использую Deepl, очень бодрый и качественный перевод.
TOC:
Categories of legitimate reservations
- Known logical diagrams not exactly logical, because they don’t address the issue of connections between one or several elements.
- CLR actually differentiates one’s perception from the way things really are.
- It tests cause and effect with several specific tools. They all circle around effects of causation.
- Clarity.
- good communication
- Entity existence. Where entity is a statement, logical and complete without grammatical mistakes, that understandable at the first glance and doesn’t imply several ideas and has not if-then assumption.
- Causality existence.
- Cause insufficiency.
- Additional cause.
- Cause and effect reversal.
- Predicted effect existence.
- Tautology.
- Clarity.
- CLR can be applied for
- to check soundness of a built tree by tree builder and scrutinizer (a person who searches flaws in the logical construction)
- It tests cause and effect with several specific tools. They all circle around effects of causation.
- CLR actually differentiates one’s perception from the way things really are.
Builder and scrutinizer look like debating people? (from my ideas about knowledge creation systems) They not openly oppose each other, but one tries constantly disrupt ideas of the other. But in the case of building trees only one has ideas, the other one is checking ideas from every possible angle. Attacks them, if you wish.
Builder wants to construct a tree and present at some point in time, creator loves his creation, and he is touchy about his work. Though he can accept sound advice, it is important to present it in a non-threatening way. Those who check trees for consistency must do it from a supportive position and have substantial expertise in the field in question.
In order to be understood presenter or lector should understand himself. Like Feynman used to say, that when he wrote the curricular for beginners physicist class, if he can’t explain complex principle in simple words it only means that his knowledge of the topic not complete.
It’s not important to reach an agreement in argument. More important is to find an agreement in definitions.
Listener’s problems of understanding are:
Meaning, significance, context of meaning, cause and effect, missing not mentioned steps (intermediate)
You should always remember that in order to be logical entities have to express
- a complete idea
- subject and verb, sometimes objects are OK. Remember the story about moon landing module. Personal pronouns are only acceptable.
- It, this and those are signal of bad logic
- be grammatically sound and correct,
- do not include several notions and be atomic,
- exclude if-then ideas and should be valid at the first glance.
Simplicity is the mean for building sound trees.
-
Adherence to the rules is important for building
-
Apply validity test to conditions of reality not actions.
-
For checking cause and effect occurrences builder and scrutinizer have to check effects of one thing on another and be able to look beyond of what is stated in the beginning.
-
Some of the cause and effect situations are unobservable and can represent biased opinion of a builder.
How to protect oneself from biases?
-
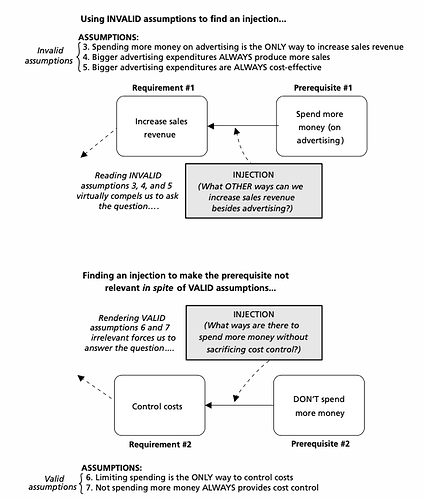
Cause insufficiency is the most common defect in logical trees.
-
Rule of thumb limit the number of arrows to four. Each additional arrow brings less valuable information and has less important cause in its core. Four arrows are optimal.
- If you absolytely can’t avoid using four or less arrows, put every additional arrow as a different cause.
-
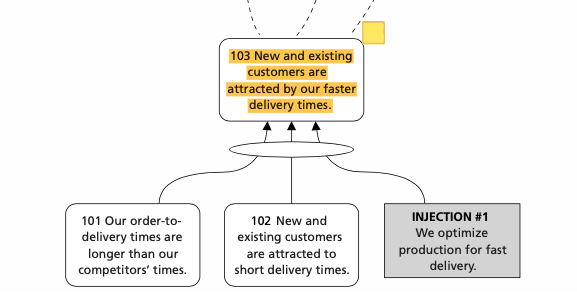
Simple casualty one arrow cause and effect
-
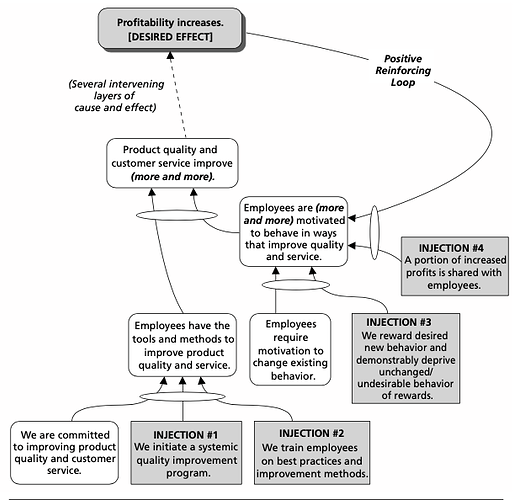
complex casualty, multiple arrows from multiple causes to single effect.
- Each may add magnitude to another and create cumulative effect.
-
Best way to check cause and effect through a question. What if existing causes not all that there is, and maybe we should look for some additional causes.
-
There might be simple and complex causality
- Simple one arrow cause and effect
- multiple arrows from multiple causes to a single effect. Each may add magnitude to another and create cumulative effect.
If we predict that some cause and effect relationship is valid that means there are some unstated cause and effect might exist.
- Expectation
- Is it there?
- Proposed effect.
- Coexistence
- Is it there at the same time?
- proposed effect and existing effect coexist.
Circular logic (Tautology).
To avoid ask questions
- Is this cause intangible?
- Is the effect ordered as a rationale for the existence of the cause?
- Are there any additional predicted effects that could substantiate the tangible cause?
The more men in a CLR group then worse doesn’t matter that all of them understand rules of tree building, cause and effect and what sound logic mean. If only one person (tree builder) knows rules of CLR it could turn into advantage.
I won’t write extensive notes on the third chapter Intermediate Objectives map for several reasons:
- Chapter isn’t big.
- I’ve drawn a beautiful mindmap.